B2B integration has upended enterprises of different sizes, yet there are many who have stumbled during execution. The real reason being lack of understanding. Therefore, it’s important for enterprises to understand the key concepts behind this trend. We asked our experts more about this approach. Knowing these details can help enterprises remove fear, uncertainty & doubt and embracing B2B integration platforms with confidence.
IMAGE: ADEPTIA.COM
What Is B2B Integration?
B2B integration involves the integration of B2B/EDI processes with partner communities via a single, flexible B2B platform. This platform automates B2B processes for better governance and visibility. It also supports many electronic data interchange (EDI) protocols and communication protocols to ensure high availability of operations.
B2B integration inherently involves automation of manual business operations. Some of the best examples in this regard are web services that have replaced Fax machines and telephones.
Another great example is EDI, a series of messaging standards that have replaced paper-based communication across many industries.
How Does B2B Integration work?
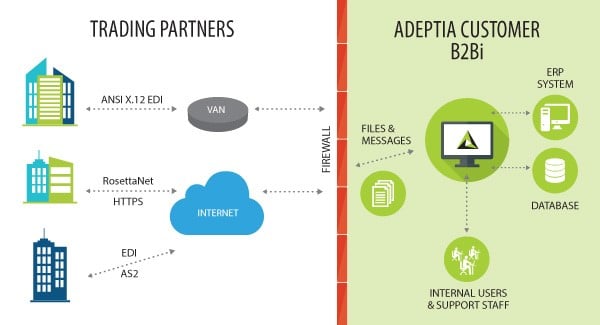
In a streamlined B2B ecosystem, data, i.e., purchase orders, invoices, sales receipts, etc., from the source system is mapped to an industry standard. These messages are then delivered via a messaging standard like AS2 or SFTP. Sometimes these standards are dictated by trading partner. All this mapping, translation, and delivery is executed via a gateway. This centralized gateway makes it easier for business communities to exchange business data in a strategic manner. Here are some important elements of B2B integration.
Source Application – Data originated in a source application or front-end system is extracted for business use. This data extracted can be a purchase order (PO), invoice, receipt, etc.
Data Format – Extracted data is normalized into a standardized format like EDI, XML, CSV, JSON, etc. This allows for integrating data with other applications. Data mapping capability is essential for mapping continuous streams of data.
Transport Protocol – A transport mechanism is determined to send messages. Workloads must be evaluated before defining a transport channel.
Target Application: The final element of B2B framework is a target application where the data needs to be moved. This application needs to be able to receive data and map this data into a normalized standard for ingesting it across the ecosystem.
Disadvantages Of Manual B2B Integration Approaches
Lack of Drivers for Exception-Handling – Manual scripting and home-grown approaches don’t provide appropriate drivers for exception handling. That’s why it becomes hard to monitor and resolve exceptions or breakdowns on time. This inability causes B2B errors which result in hefty charge-backs, delays, and revenue losses. There is zero visibility to data, monitoring the data flows becomes a big challenge.
Data Access – With manual approaches, it becomes difficult to get access to data siloed in different IT systems. Defragmented systems and silos prevent teams from bringing data to the right place at the right time. Teams fight lengthy battles in connecting legacy applications with cloud applications and getting access to data.
Resilience/Recovery – It is impossible to create high resiliency B2B networks with home-grown approaches. Multiple end-points and connections pose redundancy challenges when mission-critical data needs to be replicated to the backend. Enterprises face difficulties in handling the range of issues while recovering databases from disasters that disrupt business continuity.
All these challenges can be fixed with an automated b2b integration strategy. Teams can combine business systems and eliminate silos. Partners get the ability to exchange data without complex and lengthy lines of coding.
If you are interested in even more business-related articles and information from us here at Bit Rebels then we have a lot to choose from.

COMMENTS